Timing Belt Simulation
DIGITAL ENGINEERING AND EVALUATION
3D Virtual Validation Model
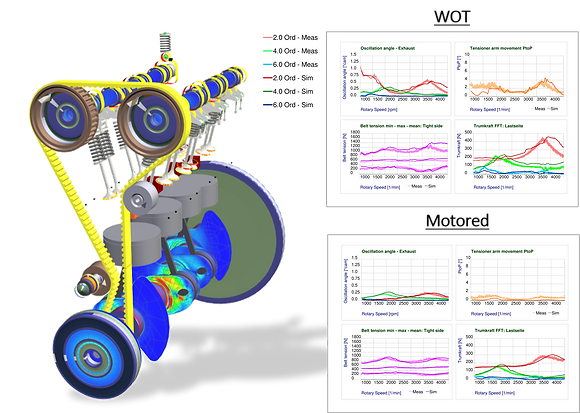
Timing belts in camshaft drives are highly reliable components - but only if they are correctly designed for all engine operating conditions. This includes ensuring that the maximum and minimum dynamic belt forces do not exceed the limits that the belt can withstand. Furthermore, maintaining the timing error, especially in the resonance of the timing drive, is of central importance for efficient motor operation. If the belt running-in into the sprocket is disturbed due to incorrect belt pitch and pretension, the belt drive becomes acoustically noticeable, which is amplified by belt flapping. If belt flapping is too high or belt force on slack side is too low, there is a risk of tooth skipping.

Our holistic engineering process
The particular challenge in designing the timing drive is that the crankshaft, camshaft and injection pumps act on the belt drive highly dynamically and with arbitrary phasing, so that the system can only be reliably optimized using a complete engine model with all interactions.
This multi-dimensional design process is fully mapped with our optimization tools, whereby all component and material properties are taken into account in detail:
-
Timing Belt Master Parameter
-
Sprocket geometry (round and un-round)
-
MBS models for tensioning systems
-
MBS model for cam-phaser
-
MBS model for valve train
Case Study Noise | 19th Order Evaluation
Prerequists
-
Predicted system behavior of timing drive simulation shows excellent match with measurement results
-
All components very well known and understood in detail
-
Engine shows whining noises on test rig
-
Critical whining effect can be reproduced



Countermeasures | Particle swarm optimization
Several parameters were changed at the same time in parameter study
-
Particle swarm optimization (PSO), inspired by nature and evolutionary swarm intelligence and swarm movement
-
Typical field of application: Topology optimization and parameter identification
-
Optimization goal: Reduce order 19 as much as possible (210 single simulations – Convergence reached after 40 simulations)
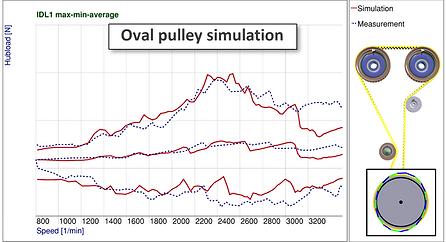
Simulation measurement comparison | Oval Pulley Design
-
Hub load level measured at idler pulley
-
Dynamic characteristic shows very good correlation with and without oval pulley usage
-
Oval pulley phase was proposed by calibration experts -> Effect not good enough -
Oval pulley phase was improved in simulation and verified on test rig